What Is SCORM?

SCORM (Shareable Content Object Reference Model) is a collection of standards and specifications for web-based eLearning products. The standard provides the communication method and data models that allow eLearning content and an LMS to be able to work together. It tells programmers how to write code so that what they build will be compatible with […]
What Is Crowdsourced Learning?

Crowdsourced learning is learning content requested, developed, and delivered by a group of individuals not normally tasked with creating learning content. Crowdsourced learning need not be sourced from a specific set of designated learning and development professionals or instructional designers. Instead, crowdsourced learning originates from anyone within a department or company who can provide meaningful, […]
What Is a Learning Objective?

A learning objective describes what learners should know or be able to do at the end of the course that they couldn’t do before. A learning objective should clearly define the expected outcome of a course in terms of demonstrable skills or knowledge that will be acquired by the learner as a result of the […]
What is Mobile Learning?

Mobile learning, or m-learning, is the delivery of learning content via any endpoint of the user’s choosing. Mobile learning is convenient, as it is available anytime, anywhere: courses can be accessed via smartphone, tablet, laptop, or any other device. That learning in the workplace is taking place on a mobile device should come as no […]
What is Design Thinking?

Design thinking is a process that focuses on the user, challenges assumptions, and redefines problems in an attempt to identify alternative strategies and solutions that might not be instantly apparent with an initial level of understanding. It is a way of thinking and working, and a collection of hands-on methods. The Five Phases of Design […]
What is the Magic Triangle: Aligning Learning Objectives, Training Activities and Assessment Methods
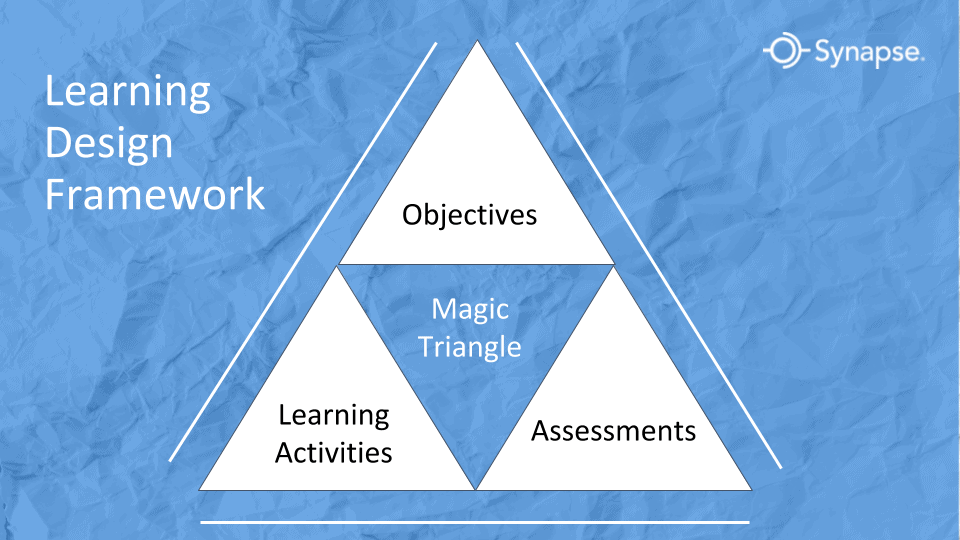
The Magic Triangle represents the relationship between Learning Objectives, Learning Activities, and Learning Assessment. If these three components are built with the intention of interdependence, then instructional design and learning are greatly enhanced and superior outcomes are achieved. If one or more of these three components is not optimal, then learners become discouraged, confused, bored, […]
What is a Learning Design System?

A Learning Design System (LDS) is a platform that automates and streamlines the instructional design process. Best practices in adult learning theory are baked into the system to empower training departments to create high-quality training in a scalable way. By focusing on the front-end of training program development, which includes items such as goal and […]
What is xAPI?

The Experience API (or xAPI), in general terms, is a specification for learning technology that makes it possible to collect data about the wide range of experiences a person has both online and offline. According to xAPI.com, this API, or application programming interface, is a protocol that captures data in a consistent format about a […]
What is Instructional Design?

Instructional design is the practice of systematically designing, developing and delivering learning experiences. The intended result is the acquisition and application of knowledge and skills. These learning experiences could include online courses, instructional manuals, video tutorials, learning simulations, quizzes, and games. Instructional designers are considered the “architects” of the learning experience and often serve as directors and […]
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?

Bloom’s taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. The models organize learning objectives into three different domains: Cognitive, Affective, and Sensory/Psychomotor. Bloom’s taxonomy was developed to promote higher forms of thinking in education, such as analyzing and evaluating concepts, processes, procedures, and principles, rather than simply memorizing facts. […]